Urea price depends on a number of factors and you should contact us directly to obtain a current urea price at FOB or CIF terms.

Urea Price
Price of urea depends on a multitude of factors.
We currently over a 1000 mt per month consignment of urea available at FOB Baltic (FOB Ust Luga or St. Petersburg) terms. This urea comes from an ultra-reliable top-level supplier. The price is not rock-bottom but it is real. That makes all the difference.
Secondly,
We have offers of urea in excess of 10 000 mt per month, from suppliers in the Russian Federation and Central Asia (Turkmenia, Turkmenistan), likewise at FOB terms, at attractive prices with large quantities, but the genuineness of the offers must still be verified.

Please contact us for up-to-date information on urea pricing and send you whatever inquiries you may have.
For urea use email address urea at russiancommerce.ru
Thank you.
End of the message.

Prior (older) posts:
Silica Sand Quarry
Silica Sand Quarry. Quartz Sand Quarry Industrial Sand Quarry. These are the same things – silica sand quarry or quartz sand quarry or an industrial sand quarry. An area comprising…
LME London Metal Exchange — what is it and how does it make money? Secrets Revealed.
LME London Metal Exchange — what is it and how does it make money? Secrets Revealed. LME London Metal Exchange — what is it and how does it make money?…
1. Swiss Offshore Banks – A Swiss Offshore Bank for Sale but better be aware of blacklisted cash.
Swiss Offshore Banks. Swiss Offshore Bank for Sale. At this price a giveaway to the qualified party. But read our disclaimer and commentary. For the ad itself without disclaimers and…
Urea fertilizer for export
Urea fertilizer for export. Wanted urea for export. We have certain suppliers of urea from Russia but we also have buyers with requests for enormous quantities of urea. We are…
Bank for sale in Germany
Bank for sale in Germany. Bank for sale in Germany. BaFin Regulated Fully Licensed German Bank For SaleCommercial Banks, Savings Banks – Germany Setting up a Bank in Germany, one…
US Bank for sale in Puerto Rico
US Bank For Sale in Puerto Rico (IBE not IFE) Commercial Banks, Savings Banks – United States – $25,000,000 USD A very rare opportunity is available in the US…
Aviation Jet Fuel for Sale
Below is a sample of jet fuel from Rosneft. FOBAdditionally jet fuel is available from several other suppliers. Airline jet fuel for sale. We have a number of sources globally…
First Steamboat in Russia
First Russian Steamboat or the history of steamships in Russia The first steamboat in Russia was built at the Charles Byrd factory in 1815. It operated between St. Petersburg and…
Brick Manufacturing in the 18 century Russia
Brick manufacturing and Brick Making in the 18th century Russia. Procurement of building materials is the most important task facing the organizer of stone construction work. The list of basic…
Cast and Pig Iron
A history of cast and pig iron production in the Russian context. Export of pig iron and cast iron. If you need actual pig iron or cast iron from Russia,…
History of Exchanges and Bourses in Russia (part 3)
continued History of Exchanges and Bourses in Russia. Compared to other exchanges – either in Western Europe, in Paris and London, or in New York across the Atlantic, or in…
Bourses and Exchanges in Russia (part 2)
continued from Bourses and Exchanges: Russia’s third bourse, in Warsaw, was chartered in 1816. A small mercantile exchange was incorporated in the town of Kremenchug in a central part of…
Exchanges and Bourses in Russia (Part I)
Exchanges and Bourses, a History. Exchanges and bourses in Russia have a long history. St. Petersburg exchange is no longer extant as the Bolsheviks had abolished the old exchange and…
World pollock prices
World pollock prices collapse due to (again!) erratic behavior of the Chinese. On the hand, after 200 or so years China is now a superpower, and it can afford to…
River Perch
We had quite a few indirect inquiries to buy river perch from Russia. The perch in question is sweetwater Eurasian perch, also known as European perch or perca fluviatilis. The…
What is a trade lead?
What is a trade lead? What are trade leads? A few people asked me what is a trade lead. Informal English is good or maybe the more appropriate word here…
Buy Cathode Copper – a trade lead
Buy cathode copper. We have a client looking for cathode copper or copper cathodes from the Russian Federation or, under some circumstances, Kazakhstan. The material must be offered at FOB…
Silica Sand Quarry
Summary A silica sand quarry or a quartz sand quarry for sale in the St. Petersburg region (Leningrad region, Leningradskaïä oblast’). Silica Sand Silica sand is also known as…
Diesel Fuel FOB sale with CIF options.
Diesel Fuel FOB ULSD – for Sale at FOB St. Petersburg. A client of the Russian Commerce Agency, a major corporation, currently offers diesel fuel for sale at FOB St….
A free (so far) trade board for free trade
The problem with those trade boards is that most of them or all of them charge subscription fees for access. Even the BBS sites. They want money upfront while promising…
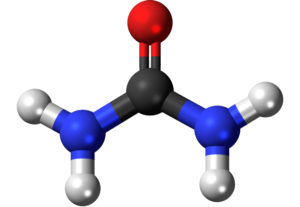
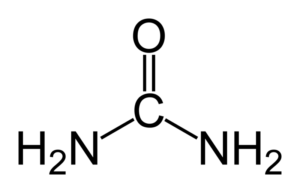
Explanation and definition of urea:
Urea
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. The material occurs not only in the urine of all mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration. In the course of the breakdown of proteins, amino groups (NH2) are removed from the amino acids that partly comprise proteins. These amino groups are converted to ammonia (NH3), which is toxic to the body and thus must be converted to urea by the liver. The urea then passes to the kidneys and is eventually excreted in the urine.
Urea was first isolated from urine in 1773 by the French chemist Hilaire-Marin Rouelle. Its preparation by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler from ammonium cyanate in 1828 was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a naturally occurring organic compound from inorganic materials.
Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide. These two materials are combined under high pressures and elevated temperatures to form ammonium carbamate, which then decomposes at much lower pressures to yield urea and water.
Urea reacts with alcohols to form urethanes and with malonic esters to give barbituric acids. With certain straight-chain aliphatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives, urea forms crystalline inclusion compounds, which are useful for purifying the included substances.
What is Urea 46 in export trade?
Urea price
Urea is one of the most important fertilizers today. It is also remarkably unstable price-wise or has been instable for the past year or so. This reflects overall market instability. Below is a sample news item, showing that in some countries government is asked to rein in surging urea prices.

Urea price.
Chinese regulators move to rein in surging urea prices after probe
China’s top economic planner and market regulator vowed on Monday to strengthen market regulation and crack down on urea hoarding and other illegal activities, in a bid to rein in surging prices of the fertilizer following an investigation into to market. Urea price is of a concern.
Price of urea FOB
The National Development and Reform Commission and the State Administration for Market Regulation conducted a field research in Central China’s Henan Province and North China’s Hebei Province to learn about the supply and demand of urea, market prices, business operations and exports.
After visiting the Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange in Henan, urea producers and agricultural material stores, the two agencies said that they would strengthen regulation and firmly crack down on activities such as hoarding and price gouging to safeguard market order and maintain price stability. Urea price and instability.
The average price of urea in China has jumped about 56 percent so far this year to 2,800 yuan ($433.73) per ton, which has increased the costs of grain planting for farmers.
Following the regulators’ inspections, the most actively traded urea contract on the Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange fell 3.06 percent to 2,247 yuan per ton on Monday.
Surging coal prices, combined with maintenance work at urea production plants, have pushed up fertilizer prices, media reports said. Surging urea prices.
Expectations of higher grain yields by Chinese farmers have also affected the market for fertilizers, Li Guoxiang, a research fellow at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, told the Global Times on Monday.
In addition, India’s reduced urea output due to the COVID-19 pandemic has led to increasing global demand from China, a major urea producer. Urea prices and PRC
According to official data from Chinese customs, China exported 3.67 million tons of fertilizers in May, the highest in two years.
The move on Monday followed earlier measures to cool rising prices of agricultural materials by various government agencies ahead of demand peaks for urea and other fertilizers in June and July.
The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and other agencies on June 17 issued a document to enhance fertilizer supply to safeguard the production of summer grain crops. Urea price and India.
“Since the spring seeding, multiple factors including short supply of raw materials and their surging prices have pushed up fertilizer prices in China by about 30 percent year-on-year, reaching a historic high,” read the document. Urea price.
It asked relevant departments to strengthen monitoring and early warnings and to adjust fertilizer supply during the summer in order to secure the summer grain crops. Urea price.
Meanwhile, on June 18, the State Council, China’s cabinet, said that the central government would allocate 20 billion yuan in subsidies to farmers in response to price hikes of agricultural materials. Urea price and inflation.
Li said that fertilizer price hikes in China are a short-term issue, as the country’s production capacity for fertilizers remains stable and demand will fall once the seeding of autumn grain crops finishes. Urea price.